About NoOps
The Future of Operations in the DevOps Era
NoOps
NoOps (No Operations) is an IT paradigm focused on automating all aspects of software deployment and operations to the point where a dedicated operations team is no longer necessary. The concept extends the principles of DevOps by pushing automation to the extreme, where developers handle the full lifecycle of an application, including infrastructure management, monitoring, and updates, through sophisticated automation tools and CI/CD pipelines. This approach relies heavily on cloud-native technologies, infrastructure as code (IaC), and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) solutions, enabling rapid deployment and scaling with minimal human intervention. While NoOps is ideal for highly automated environments, it may not be suitable for all organizations, particularly those with complex legacy systems.

Why NoOps
NoOps is embraced to streamline software development and deployment by automating operational tasks, thereby reducing the need for a dedicated operations team. The primary motivation behind NoOps is to enable faster, more reliable software delivery by minimizing human intervention and eliminating bottlenecks associated with traditional operations. In a NoOps environment, developers use advanced automation tools to manage infrastructure, monitoring, and deployment processes, allowing them to focus more on coding and less on operational concerns. This approach reduces human error, accelerates release cycles, and improves scalability and flexibility, especially in cloud-native environments. By automating operations, NoOps aligns closely with business objectives, promoting efficiency, reducing operational costs, and supporting continuous delivery and innovation. While ideal for modern, automated environments, NoOps may require a significant investment in automation tools and may not suit all organizations, particularly those with complex legacy systems.
Key Characteristics of NoOps
NoOps is characterized by several key features that collectively streamline IT operations and enhance efficiency. At its core, NoOps relies on full automation to manage routine tasks such as deployment, monitoring, scaling, and backups, significantly reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring greater consistency and reliability. It leverages cloud-native technologies, including serverless computing and managed services, which abstract away the complexities of underlying infrastructure management, allowing teams to focus on higher-level functions. Integration with Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines is another crucial aspect of NoOps, as it automates the processes of building, testing, and deploying code changes, thereby streamlining the development lifecycle. Additionally, NoOps environments are designed with self-healing capabilities, enabling systems to automatically detect and recover from failures without human oversight, further enhancing operational resilience and reliability.

NoOps Architecture
This diagram illustrates a NoOps architecture, where the majority of operational tasks are automated, minimizing human intervention. It begins with a developer committing code to a version control system, which then triggers the CI/CD pipeline. This pipeline automates various processes, including building, testing, and deploying the code. Once the code is deployed, the cloud infrastructure becomes the central hub, supported by various automation mechanisms.
AI-powered monitoring continuously analyzes the infrastructure to ensure smooth operations, while infrastructure as code defines the system setup, ensuring consistency and scalability. Serverless computing further enhances the efficiency of resource management, and continuous optimization helps in improving the performance of the cloud infrastructure.
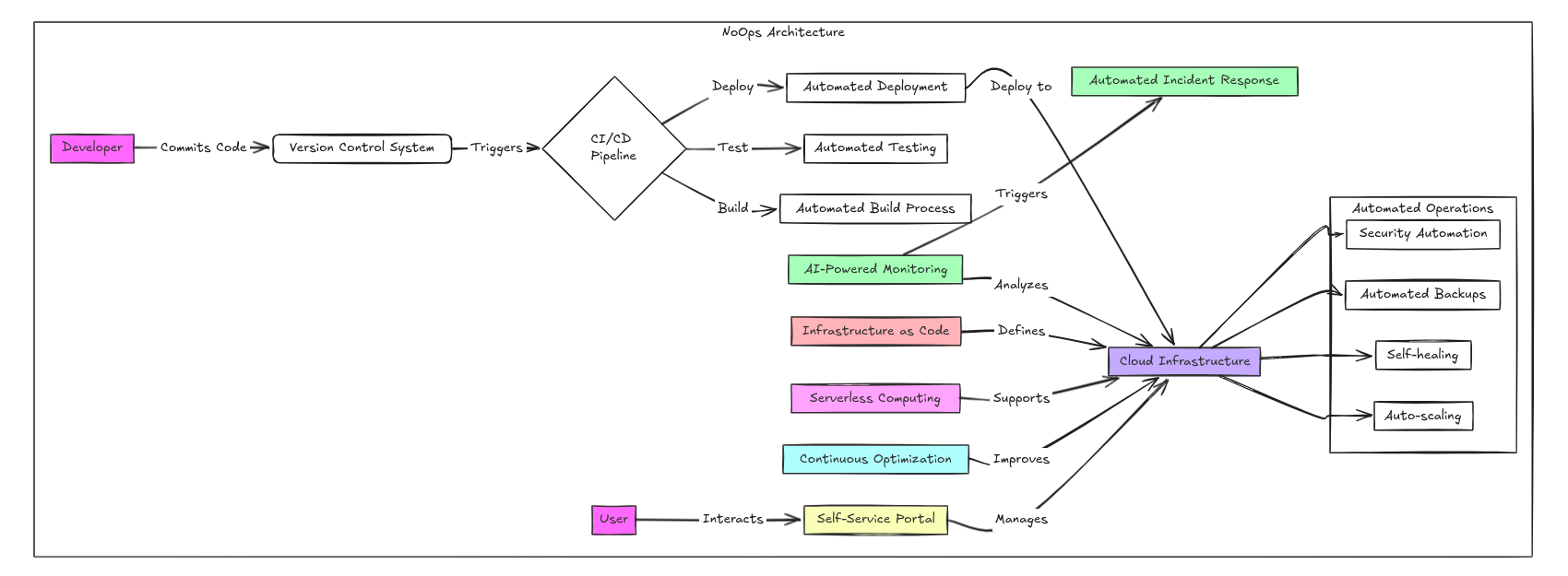
This architecture also includes several important features for infrastructure management. Automated incident response quickly handles issues as they arise, ensuring minimal downtime. Automated operations and security automation safeguard the system, while automated backups ensure data integrity. Self-healing and auto-scaling mechanisms allow the infrastructure to adapt and recover from issues on its own, maintaining optimal performance without manual intervention.
Users interact with the cloud infrastructure through a self-service portal, giving them the ability to manage resources and make changes without needing direct support from the operations team. This highly automated system forms the backbone of a NoOps environment, where manual operations are largely replaced by smart, automated processes.
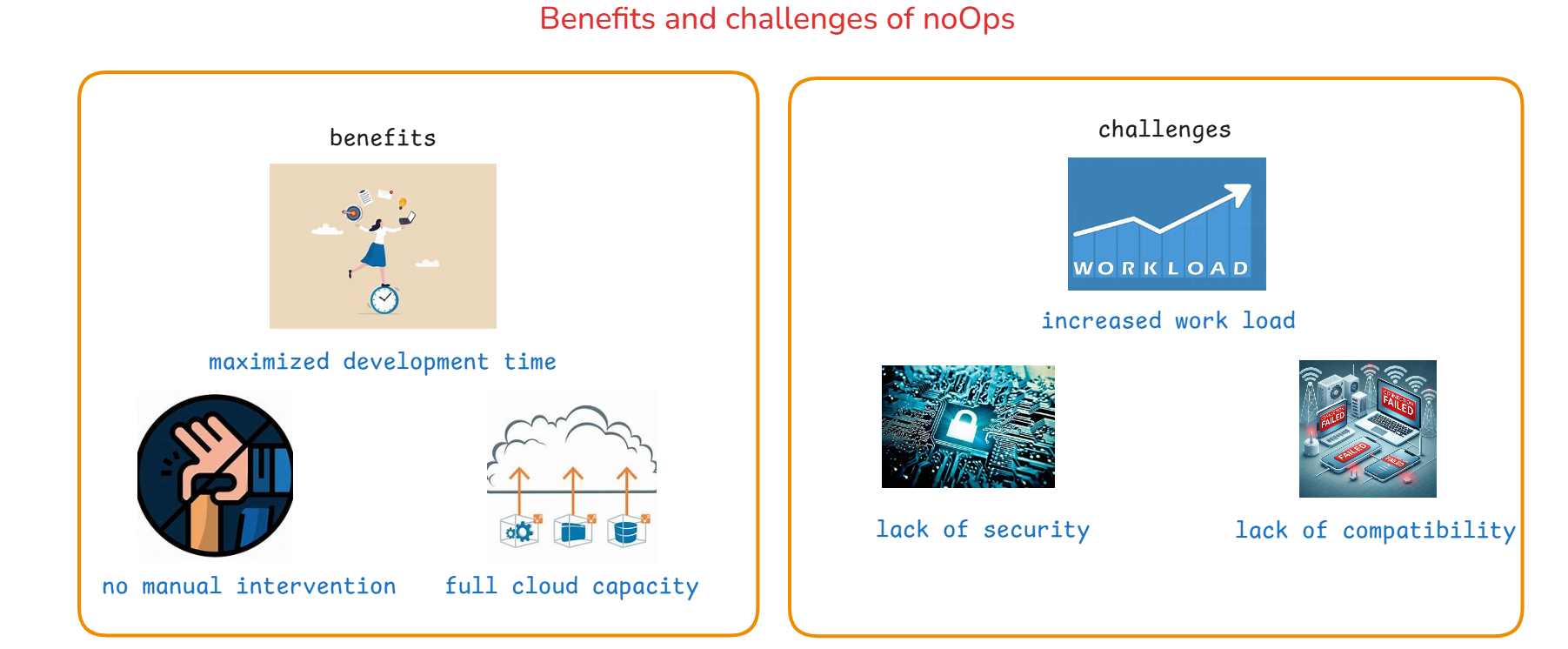
Benefits and Chalenges of NoOps
NoOps vs. DevOps
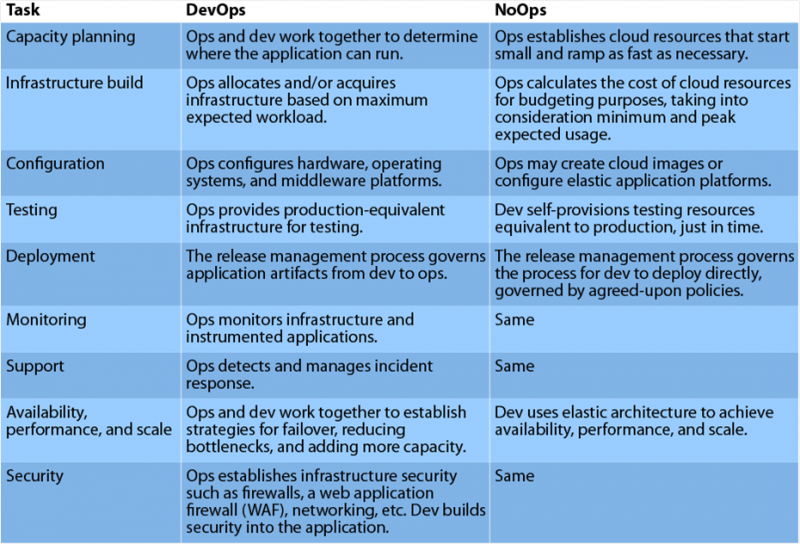
While NoOps and DevOps share the goal of improving operational efficiency, they differ in their approach. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to streamline processes, whereas NoOps focuses on automating operations to the extent that it minimizes the need for manual intervention. In a DevOps environment, operations teams play a crucial role in managing and maintaining systems, whereas in a NoOps model, many of these responsibilities are automated, leading to a more streamlined and hands-off approach.
From Manual Management to Automated Efficiency
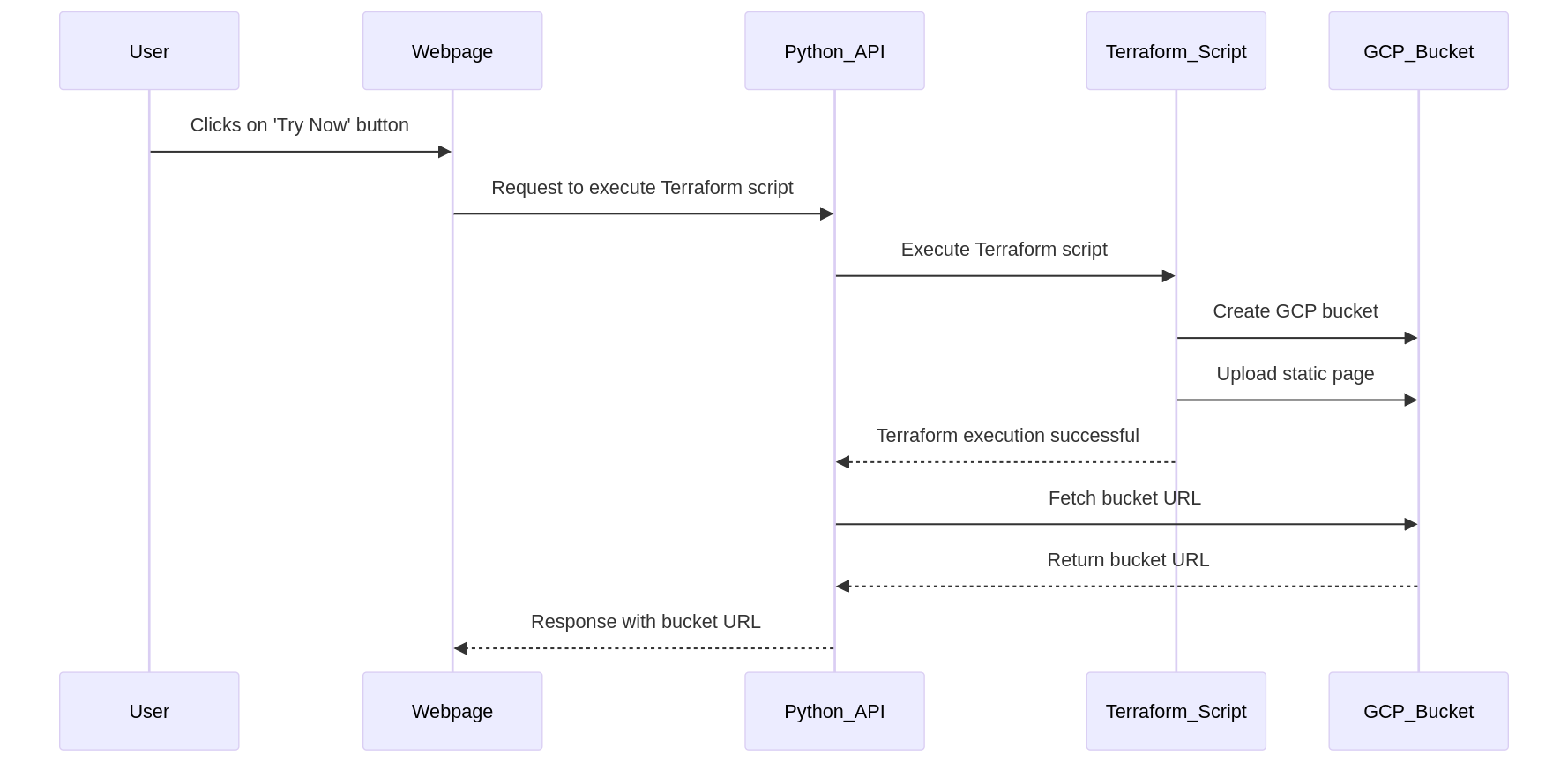
If you want to test that how automation works then you can click on "Try Now" button below, a process runs in the background to create and host a static web page on Google Cloud. Here's how it works:
First, a Python API is triggered. This API uses Terraform, a tool for automating cloud infrastructure, to create a Google Cloud Storage bucket. The bucket will store the static web page. Once the bucket is successfully created, the static page is automatically uploaded to it. Terraform ensures the bucket and its contents are publicly accessible so that anyone with the URL can view the page.
After Terraform completes the process, the Python API retrieves the URL of the newly created bucket. This URL is then returned to the web page, allowing you to view the hosted static page. All of these steps are performed automatically without any further input required from you. Simply click "Try Now," and in a few moments, you'll have access to the hosted page URL.
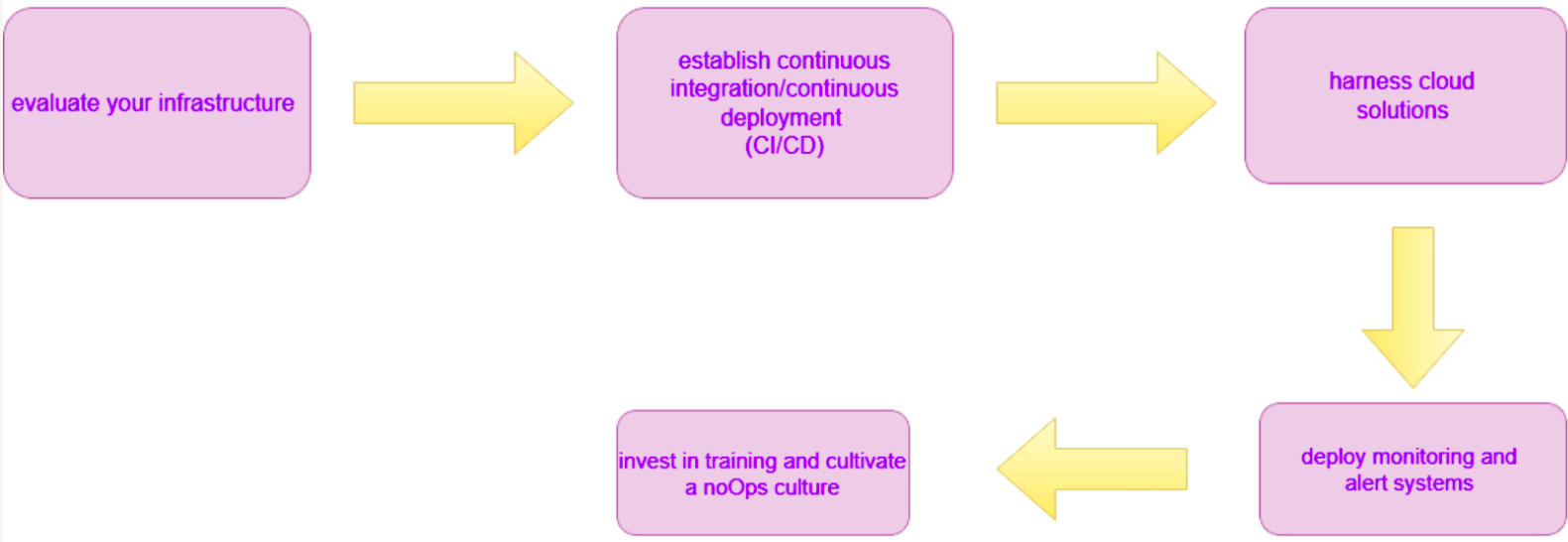
How to get started with NoOps